1. Chmod
- chmod - means that Change Mode. It is a command that controls the users permission on the file or directory in Linux.
- File accessing permissions of Linux/Unix are divided into three levels: file owner(Owner), user group(Group), and other users(Other Users).
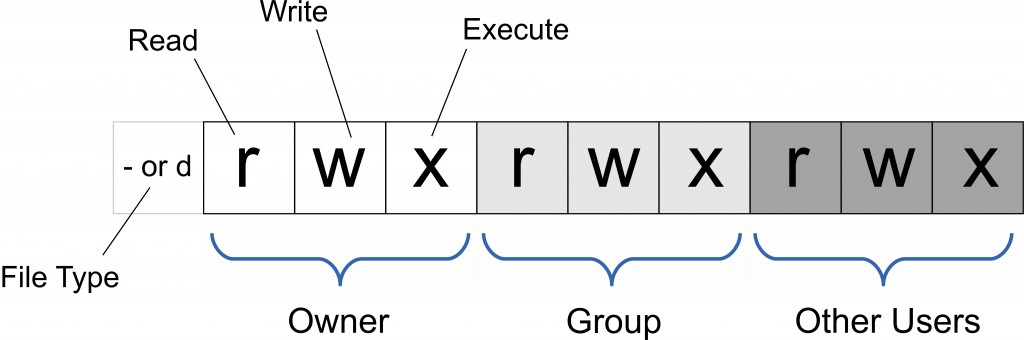
The permission of the file or directory can be changed only by the owner or the superuser, others can’t. There are two types model followed to specify the permissions.
Octal Model and Symbolic Model
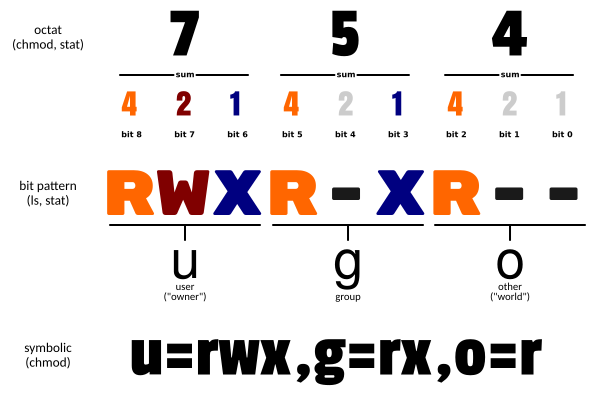
Octal File Permissions Table
Number Permissions rwx Binary 7 Read + Write + Execute rwx 111 6 Read + Write rw- 110 5 Read + Execute r-x 101 4 Read-only r– 100 3 Write + Execute -wx 011 2 Write-only -w- 010 1 Execute-only –x 001 0 None — 000
1 | touch sample.sh |
Output: -rw-rw-r-- 1 raman raman 0 三 31 14:07 sample.sh. Here, the first character (-) means it is a file.
When you create a file using touch command by default the permissions will be 664(-rw-rw-r–).
Changing the permissions to all(user, group, others).
1 | chmod -v 777 sample.sh |
Output: -rwxrwxrwx 1 raman raman 0 三 31 14:11 sample.sh*
1 | mkdir sample |
Output: drwxrwxr-x 2 raman raman 4096 三 31 14:26 sample/. Here, the first character (d) means it is a directory.
When you create a file using touch command by default the permissions will be 775(drwxrwxr-x).
For changing permissions multiple files or directories,
1 | chmod -vR 777 directory_path/* #for directories |
2. Chown
chown - means that Change Ownership. This command is used to change the owner of the file or the directory.
chown requires the permission of superuser(root) to execute it.
1
2touch sample.sh
llOutput:
-rw-rw-rw- 1 raman raman 0 三 8 00:35 testfileChanging the ownership from raman to jenkins.
1
2sudo chown -v jenkins:jenkins sample.sh
llOutput:
-rw-rw-rw- 1 jenkins jenkins 0 三 8 00:35 testfileFor changing permissions multiple files or directories,
1
2chown -vR username:usergroup directory_path/* #for directories
chmod -vR username:usergroup file_name/* #for files
